What Are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent one of the most significant breakthroughs in artificial intelligence in recent years. These sophisticated AI systems are trained on massive amounts of text data—often hundreds of billions of words from books, websites, scientific papers, and more—to understand and generate human-like text with remarkable fluency and coherence.
Unlike traditional software that follows explicit programming rules, LLMs learn patterns, context, and relationships within language through a process called deep learning. This enables them to perform a wide variety of language tasks, from answering questions and writing essays to translating languages and generating code, all without being specifically programmed for each individual task.
The term “large” refers to both the size of the training dataset and the number of parameters—the adjustable weights within the neural network that determine how the model processes information. Modern LLMs can have hundreds of billions of parameters, making them incredibly powerful but also computationally expensive to train and run.
How Do LLMs Work? The Technical Foundation
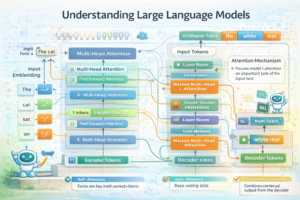
At their core, LLMs use transformer architecture, a revolutionary neural network design introduced in 2017 that fundamentally changed how machines process sequential data like text. Here’s what makes them so powerful:
The Transformer Architecture
The transformer model uses an attention mechanism that allows the AI to weigh the importance of different words in a sentence when generating responses. For example, in the sentence “The cat sat on the mat because it was comfortable,” the model understands that “it” likely refers to “the mat” rather than “the cat” by analyzing the entire context.
- Self-Attention Mechanism: Processes all words in parallel, understanding relationships between them
- Positional Encoding: Maintains understanding of word order and sequence
- Multi-Head Attention: Allows the model to focus on different aspects of meaning simultaneously
- Feed-Forward Networks: Processes the attention outputs to generate predictions
Training Process
LLMs undergo extensive training in multiple phases:
- Pre-training: Models learn language patterns from billions of text examples through unsupervised learning
- Fine-tuning: Additional training on specific tasks or domains to improve targeted performance
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Human evaluators rate responses, helping the model align with human preferences
- Continuous updates: Models are regularly updated with new data and improved training techniques
Popular Large Language Models in 2024
GPT-4 and GPT-4 Turbo (OpenAI)
GPT-4 represents the cutting edge of language model technology. Released in March 2023 and continuously improved, it offers multimodal capabilities, processing both text and images with unprecedented accuracy. GPT-4 Turbo, the latest iteration, features an extended context window of 128,000 tokens (roughly 96,000 words), allowing it to process entire books or lengthy codebases in a single prompt.
Key features include superior reasoning abilities, better factual accuracy, advanced coding capabilities, and the ability to maintain context across very long conversations. It powers ChatGPT Plus, Microsoft Copilot, and numerous enterprise applications.
Claude 3 (Anthropic)
Developed by Anthropic with a focus on safety and reliability, Claude 3 comes in three variants: Haiku (fastest), Sonnet (balanced), and Opus (most capable). Claude is particularly known for its 200,000 token context window—the largest in the industry—and its nuanced understanding of complex instructions.
Claude excels at tasks requiring careful reasoning, following detailed instructions, and maintaining consistent personality and tone. Its Constitutional AI training approach makes it particularly good at declining harmful requests while remaining helpful for legitimate use cases.
Google Gemini (Google DeepMind)
Google’s latest flagship model, Gemini, is natively multimodal, meaning it was trained from the ground up to understand text, images, audio, and video simultaneously rather than having these capabilities added later. This makes it particularly powerful for tasks that require understanding multiple types of information together.
Gemini integrates seamlessly with Google’s ecosystem, including Search, Workspace, and Android. It comes in three sizes: Nano (for mobile devices), Pro (for general use), and Ultra (for complex tasks).
Open Source Alternatives
Models like Meta’s Llama 2, Mistral AI’s Mixtral, and others are democratizing access to powerful language AI. While not matching the absolute performance of proprietary models, they offer transparency, customization options, and can be run on your own hardware, making them popular for research and privacy-sensitive applications.
Real-World Applications Transforming Industries
Content Creation and Marketing
LLMs are revolutionizing content production across industries. Marketers use them to generate blog posts, social media content, email campaigns, and ad copy at scale. While human oversight remains essential for quality and brand consistency, LLMs dramatically accelerate the ideation and drafting process, allowing content teams to focus on strategy and refinement.
Customer Service and Support
Intelligent chatbots powered by LLMs provide 24/7 customer support, handling common queries, troubleshooting issues, and escalating complex problems to human agents. These systems can understand customer intent even when questions are phrased ambiguously, provide personalized responses based on account history, and maintain context across multi-turn conversations.
Software Development
Tools like GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI’s Codex model, assist developers by suggesting code completions, generating functions from comments, translating between programming languages, and explaining complex code. Studies show developers using AI coding assistants complete tasks up to 55% faster while reporting higher job satisfaction.
Research and Education
Researchers use LLMs to summarize scientific literature, generate hypotheses, analyze data, and even draft sections of papers. In education, AI tutors provide personalized learning experiences, adapting explanations to individual student needs, generating practice problems, and offering instant feedback on assignments.
Healthcare and Medical Applications
LLMs assist healthcare professionals by summarizing patient records, suggesting differential diagnoses, explaining medical concepts to patients in accessible language, and helping with administrative tasks like documentation. While they don’t replace medical expertise, they serve as powerful productivity tools for overworked healthcare workers.
Challenges and Limitations
Hallucinations and Accuracy
Perhaps the most significant challenge with LLMs is their tendency to generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. These “hallucinations” occur because models are trained to generate coherent text, not to verify truth. They might cite non-existent research papers, invent statistics, or confidently state incorrect facts. Critical thinking and fact-checking remain essential when using LLM outputs.
Computational Resources and Environmental Impact
Training large language models requires enormous computational resources. GPT-3’s training reportedly consumed 1,287 MWh of electricity and produced 552 tons of CO2 emissions. Running these models for inference also requires significant energy, raising concerns about environmental sustainability as AI adoption grows.
Bias and Fairness
LLMs can reflect and amplify biases present in their training data, potentially perpetuating stereotypes or producing unfair outcomes across gender, race, religion, and other dimensions. Developers continuously work to identify and mitigate these biases, but it remains an ongoing challenge requiring constant vigilance.
Privacy and Security Concerns
When users input sensitive information into LLM systems, there are concerns about data privacy, especially if that information is used to further train models. Organizations must carefully consider data protection regulations and implement appropriate safeguards when deploying LLMs.
Limited Real-World Understanding
Despite their impressive language abilities, LLMs lack true understanding of the physical world. They struggle with tasks requiring spatial reasoning, understanding of cause and effect beyond what’s in their training data, and real-time information about current events unless specifically augmented with search capabilities.
The Future of Large Language Models
Multimodal Integration
The next generation of LLMs will seamlessly combine text, images, audio, video, and potentially other sensory data. This will enable applications like video understanding and generation, advanced robotics control, and more natural human-computer interaction across all communication modalities.
Efficiency Improvements
Researchers are developing techniques to achieve similar or better performance with smaller models through methods like model distillation, quantization, and more efficient architectures. This will make powerful AI accessible on mobile devices and reduce environmental impact.
Specialized Domain Models
We’re seeing growth in LLMs fine-tuned for specific industries—legal AI trained on case law, medical AI trained on medical literature, and financial AI trained on market data. These specialized models can outperform general-purpose models in their domains while being more efficient.
Enhanced Reasoning and Planning
Future models will feature improved logical reasoning, mathematical capabilities, and multi-step planning abilities. Techniques like chain-of-thought prompting are being incorporated directly into model architectures to enhance systematic thinking.
Better Safety and Alignment
As LLMs become more powerful, ensuring they remain safe and aligned with human values becomes increasingly critical. Expect more robust safeguards against misuse, better interpretability tools to understand model decisions, and governance frameworks for responsible AI development.
Getting Started with LLMs
Ready to leverage LLMs in your work or projects? Here’s your practical starting guide:
Choose the Right Platform
Select based on your specific needs: ChatGPT for versatility and widespread integration, Claude for tasks requiring very long context or careful instruction following, Gemini for Google ecosystem integration, or open-source models for customization and privacy.
Master Prompt Engineering
Learning to craft effective prompts is crucial. Be specific about what you want, provide examples of desired outputs, set clear constraints on length and format, and iterate based on results. The quality of your prompts directly determines the quality of outputs.
Understand the Limitations
Always verify important information, especially facts, statistics, and citations. Use LLMs as productivity tools and brainstorming partners, not as definitive sources of truth. Understand their knowledge cutoff dates and limitations with current events.
Develop Best Practices
Create workflows that combine AI strengths with human oversight. Use LLMs for first drafts, research synthesis, and idea generation, but maintain human review for accuracy, tone, and strategic decisions. Document what works well for your use cases.
Conclusion
Large Language Models represent a fundamental shift in how we interact with computers and process information. Their ability to understand and generate human language at scale opens up possibilities that seemed like science fiction just a few years ago. From accelerating content creation to advancing scientific research, LLMs are becoming essential tools across virtually every industry.
However, they’re not magic solutions. Understanding their capabilities and limitations, developing strong prompt engineering skills, and maintaining critical thinking about their outputs are essential for effective use. As these models continue to evolve—becoming more capable, efficient, and aligned with human values—they’ll play an increasingly central role in our professional and personal lives.
The key to success with LLMs in 2024 and beyond is viewing them as powerful assistants that augment human intelligence rather than replace it. Those who learn to effectively collaborate with AI will have significant advantages in productivity, creativity, and problem-solving capabilities. The future belongs to humans who can skillfully work alongside artificial intelligence.
Continue Learning: Related Articles
Movie Recommendation System
Hands-On Project: Movie Recommendation System
Difficulty Level: Intermediate | Duration: 3-5 hours | Topics: Collaborati…
📖 7 min read
Machine Learning with Python: Complete Beginner's Guide
Python has emerged as the undisputed leader for machine learning development, offering an ecosystem of powerful librarie…
📖 10 min read
AI-Powered Inventory Optimization for E-commerce: Reduce Carrying Costs by 40% While Eliminating Stockouts
E-commerce businesses lose $1.77 trillion globally to overstocking and stockouts combined. AI-powered inventory optimiza…
📖 16 min read
Transformer Architecture: The Technology Powering Modern AI
The Transformer Revolution in AI
In 2017, a groundbreaking paper titled "Attention is All You Need" introduced the Tr…
📖 5 min read
💡 Explore 80+ AI implementation guides on Harshith.org